10+ Mean Deviation Secrets For Faster Results
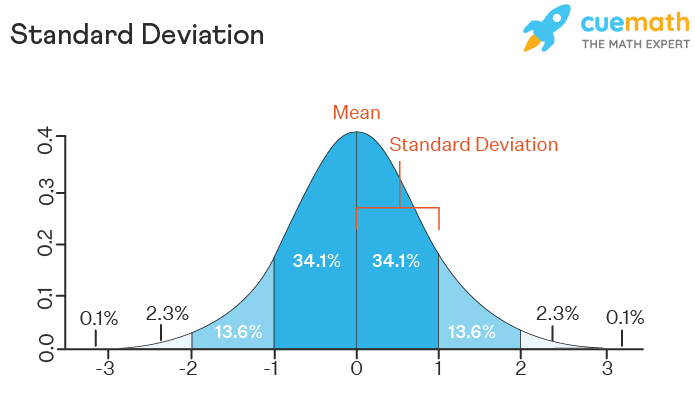
The concept of mean deviation is a fundamental principle in statistics and data analysis, representing the average distance between each data point and the mean value of a dataset. Understanding and applying mean deviation effectively can significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of data-driven insights. In this article, we will delve into the secrets of mean deviation, exploring how it can be leveraged to achieve faster results in various analytical contexts.
Introduction to Mean Deviation
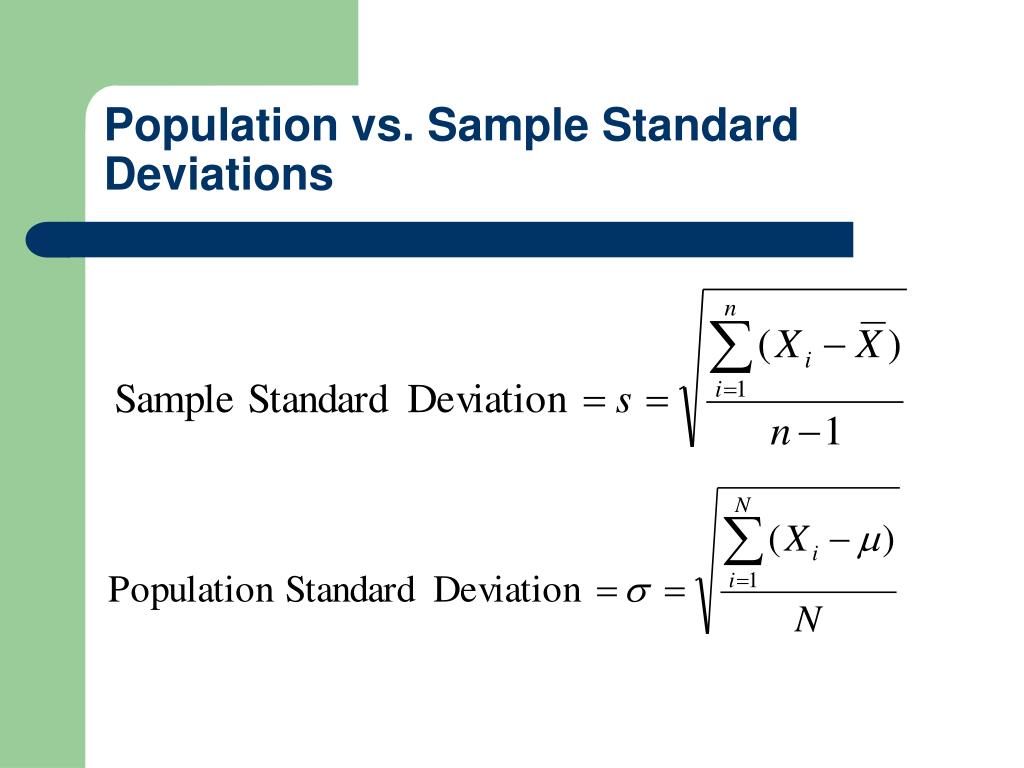
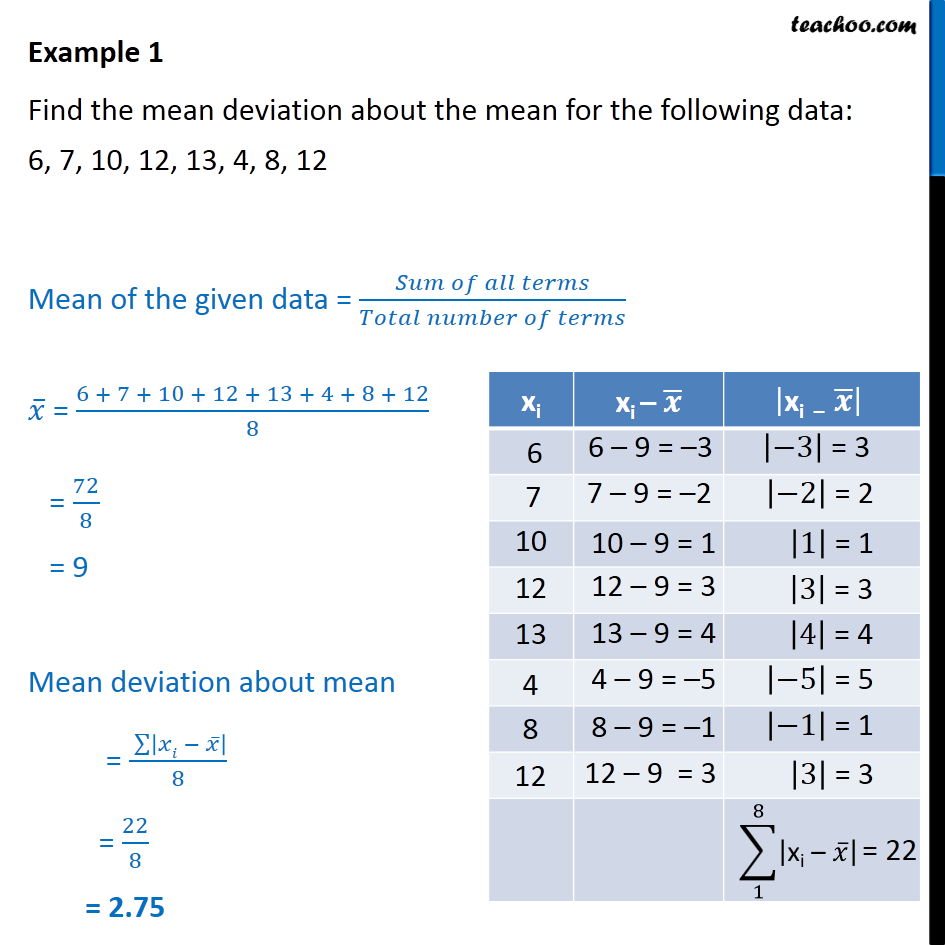
Mean deviation, also known as the mean absolute deviation (MAD), is a measure of the spread or dispersion of a set of data from its mean value. It is calculated by taking the average of the absolute differences between each data point and the mean. The formula for mean deviation is MAD = Σ|xi - μ| / N, where xi represents each data point, μ is the mean, and N is the total number of data points. Understanding the mean deviation is crucial for assessing the variability within a dataset and making informed decisions based on data analysis.
Calculating Mean Deviation
To calculate the mean deviation, one must first determine the mean of the dataset. The mean (μ) is calculated as the sum of all data points divided by the number of data points, μ = Σxi / N. Once the mean is known, the absolute deviation of each data point from the mean is calculated, and these deviations are then averaged to find the mean deviation. This process can be computationally intensive for large datasets, highlighting the need for efficient computational tools or methods.
| Dataset | Mean | Mean Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | 3 | 1.2 |
| 10, 12, 15, 18, 20 | 15 | 3.6 |
Secrets for Faster Results with Mean Deviation
Applying mean deviation in data analysis can yield faster and more accurate results when done correctly. Here are several secrets to enhance the use of mean deviation:
1. Efficient Computation
For large datasets, using computational tools or programming languages like Python or R can significantly speed up the calculation of mean deviation. These tools often have built-in functions for calculating mean deviation, making the process more efficient and reducing the chance of human error.
2. Data Preprocessing
Before calculating mean deviation, it’s essential to preprocess the data. This includes cleaning the data to remove any missing or duplicate values and transforming the data if necessary to ensure it meets the assumptions of the analysis. Data preprocessing is a critical step that can affect the accuracy of the mean deviation calculation.
3. Understanding Data Distribution
Knowing the distribution of the data (e.g., normal, skewed) can help in interpreting the mean deviation. For instance, in a perfectly normal distribution, about 68% of the data points fall within one standard deviation of the mean. However, mean deviation provides a more robust measure of spread in the presence of outliers.
4. Comparison with Other Measures
Comparing mean deviation with other measures of dispersion, such as the standard deviation or interquartile range, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the dataset. Each measure has its strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right measure depends on the nature of the data and the research question.
5. Application in Real-World Scenarios
Mean deviation has practical applications in various fields, including finance, quality control, and healthcare. For example, in finance, mean deviation can be used to assess the risk of an investment portfolio by measuring the average deviation of returns from the mean return. Real-world applications of mean deviation highlight its utility and importance in data-driven decision-making.
Future Implications and Advancements
The use of mean deviation is expected to continue evolving with advancements in data analysis and machine learning. Future implications may include the development of more sophisticated algorithms for calculating mean deviation in complex datasets and the integration of mean deviation into predictive models to enhance their accuracy and robustness.
Evidence-Based Decision Making
The calculation and application of mean deviation are rooted in statistical theory and empirical evidence. By relying on evidence-based methods, analysts can ensure that their conclusions are grounded in reality and less susceptible to bias. Evidence-based decision making is critical in today’s data-driven world, where the stakes of incorrect decisions can be high.
In conclusion, mean deviation is a powerful tool for understanding data variability and making informed decisions. By leveraging the secrets outlined above and staying abreast of future advancements, professionals can harness the full potential of mean deviation to achieve faster and more accurate results in their analytical endeavors.
What is the primary advantage of using mean deviation over standard deviation?
+
The primary advantage of using mean deviation is its robustness to outliers. Since it calculates the average of the absolute differences from the mean, extreme values have less impact on the mean deviation compared to the standard deviation, which squares these differences.
How is mean deviation used in real-world applications?
+
Mean deviation is used in various real-world applications, including finance for risk assessment, quality control for monitoring production variability, and healthcare for analyzing patient outcomes. Its ability to provide a clear measure of data spread makes it valuable for decision-making in these fields.
What are the limitations of mean deviation?
+
One of the main limitations of mean deviation is that it does not provide a complete picture of the data distribution on its own. It is often used in conjunction with other statistical measures to get a fuller understanding of the data. Additionally, mean deviation can be sensitive to the choice of the central tendency measure used (mean, median, etc.).

